Beginner’s Guide to CAD: Easy to Understand, Easy to Start, Easy to Apply

If you're new to the field of engineering design, you've probably come across the term "CAD" at some point—whether during your studies, work, or software introductions. However, not everyone fully understands what CAD is, what it’s used for, the different types of CAD software, or how to choose the right one.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the basics of CAD and its practical applications across various industries—giving you a clear, easy-to-grasp overview and a smooth starting point.

1. What is CAD?
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It is an essential tool in modern engineering and manufacturing. CAD allows engineers, designers, and architects to create 2D and 3D models of products, check dimensions, simulate movement, analyze collisions, and much more—things traditional paper drawings simply can't do.
Unlike hand-drawing, CAD enables precise design down to the millimeter, allows for quick adjustments, and integrates seamlessly with CAE (engineering analysis) and CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) software.
2. Popular Types of CAD Software
CAD software is increasingly diverse, catering to different design needs across many industries. Based on modeling methods and usage purposes, CAD software can generally be divided into three main categories:
2.1. 2D CAD – Flat Technical Drawing
2D CAD software focuses on two-dimensional drawings, commonly used for technical schematics like electrical diagrams, construction plans, assembly layouts, and detailed part drawings. It’s a familiar starting point in many technical fields, allowing engineers to visualize ideas accurately and intuitively.
Key Features:
- Fast design and simple operation
- Easy to learn and beginner-friendly
- Ideal for construction, MEP, and basic mechanical design
Typical Software:
- AutoCAD – The most popular and widely accepted in the industry
- ZWCAD, DraftSight – Affordable alternatives with core functionality
2.2. Basic 3D CAD – Solid Modeling and Assembly Design
Basic 3D CAD is used for designing mechanical components, machinery, molds, and automated production systems. These tools support solid modeling, allowing precise design and part assembly. Many offer parametric design, enabling size or shape changes without redrawing.
Key Features:
- Realistic 3D modeling
- Supports multi-part assembly
- Generates technical drawings from 3D models
- Often includes simulation or CAM features
Typical Software:
- CADmeister – Specializes in mold and precision mechanical design, aligned with Japanese industrial standards. Trusted by many FDI companies in Vietnam.
- SolidWorks – User-friendly interface, widely used in SMEs
- PTC Creo, Autodesk Inventor – Strong in mechanical design with built-in analysis and simulation
2.3. Advanced 3D CAD – For Complex Industrial Design
This group of software is capable of modeling highly complex shapes with extreme precision, including surface modeling, freeform shaping, parametric modeling, and assembling thousands of parts. It’s widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical equipment industries—where form, aerodynamics, and simulation play critical roles.
Key Features:
- Designs complex, freeform shapes
- Simulates and tests products in virtual environments
- Manages design data and supports collaborative workflows
Typical Software:
- 3DEXPERIENCE CATIA – A comprehensive solution from design and simulation to product lifecycle management, trusted by leading OEMs such as Airbus, Toyota, BMW, Tesla,...
- Siemens NX – Strong in simulation and CAM integration
- Alias, Rhino 3D – Specialized in surface modeling and industrial design
2.4. CAD Data Processing Tools – Ensuring Workflow Continuity
In design and production processes, different teams often use different CAD software. Since each software has its own file format, data incompatibility can occur—leading to shape loss, dimensional errors, or modeling issues when opening files across platforms.
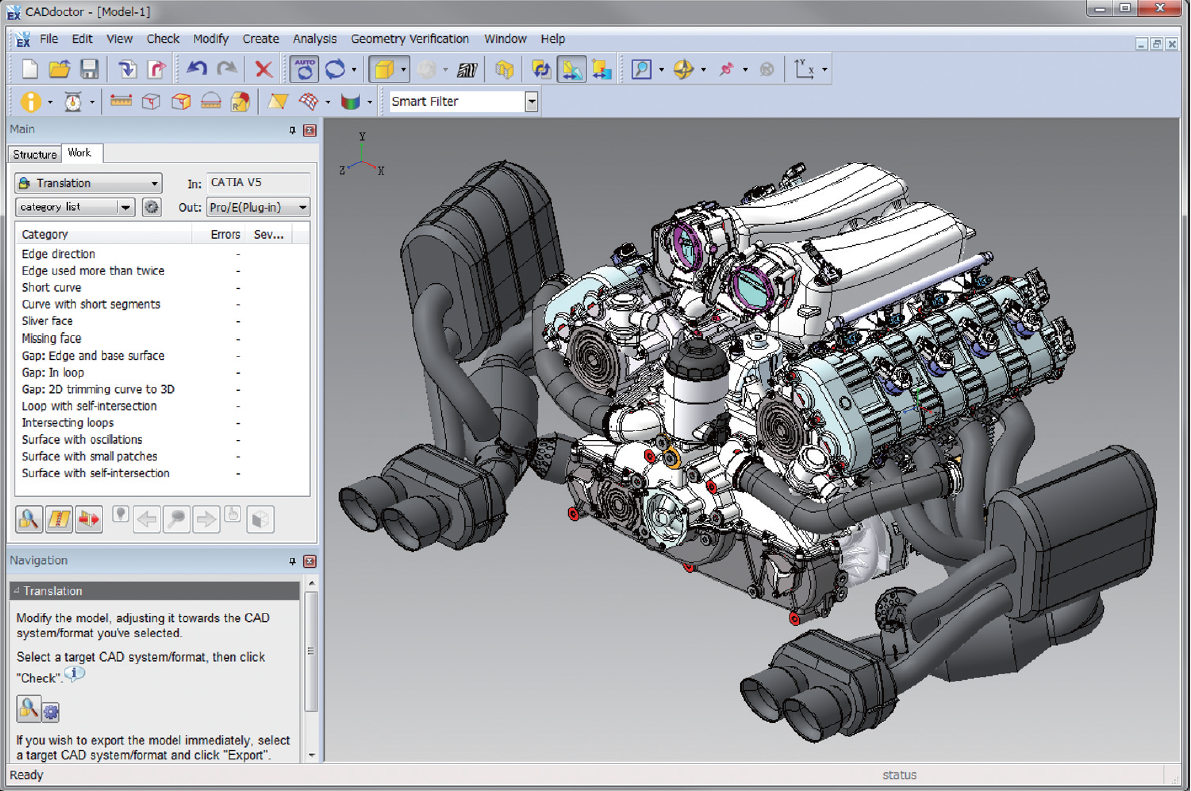
Tools like CADdoctor are built to solve this. They help:
- Detect and fix geometry errors (e.g., open surfaces, gaps)
- Convert files between formats (e.g., from CATIA to NX or SolidWorks)
- Ensure 3D model integrity when collaborating across departments or with external partners
3. Benefits of Using CAD Software
Switching from manual drafting to CAD brings substantial advantages to individuals and businesses alike. Beyond speeding up design work, CAD enables more effective management, collaboration, and product development.
3.1. Accelerated Design and Revisions
CAD lets you create technical drawings and 3D models much faster than traditional hand-drawing. Features like copy tools, parametric editing, and standard parts libraries greatly reduce drawing time, especially for modular or repetitive designs.
3.2. High Accuracy and Fewer Errors
CAD supports measurements down to microns—critical in industries requiring extreme precision like aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Conflict detection, assembly analysis, and simulation tools allow early error identification at the design stage.
3.3. Easy Editing and Reusability
Unlike paper drawings, CAD designs can be edited easily without confusion. You can save design versions, track changes, and revert when needed. CAD files are also reusable, making it easier to develop product variations and speed up R&D.
3.4. Enhanced Collaboration and Data Exchange
CAD enables team collaboration, real-time feedback, and file sharing—especially on cloud platforms like 3DEXPERIENCE CATIA. Exporting in standard formats (.STEP, .IGES, .DXF, etc.) ensures smooth data exchange with clients, suppliers, and other software.
3.5. Integration with Manufacturing and Simulation
Many CAD tools are integrated with CAE (simulation) and CAM (machining), creating a seamless flow from concept to real product. This integration helps companies reduce costs, shorten time-to-market, and optimize production workflows.
4. Industries Where CAD Is Widely Used
CAD is no longer confined to mechanical design departments—it plays an essential role across many modern industries. Here are the most common CAD applications in Vietnam and globally:
4.1. Mechanical Engineering & Manufacturing
The top user of CAD, from tiny parts like shafts and gears to large machines and entire assembly systems. Engineers use CAD to create technical drawings, 3D models, and tolerance calculations. Tools like CATIA 3DEXPERIENCE and CADmeister are favored for large assemblies and high-precision mold design.
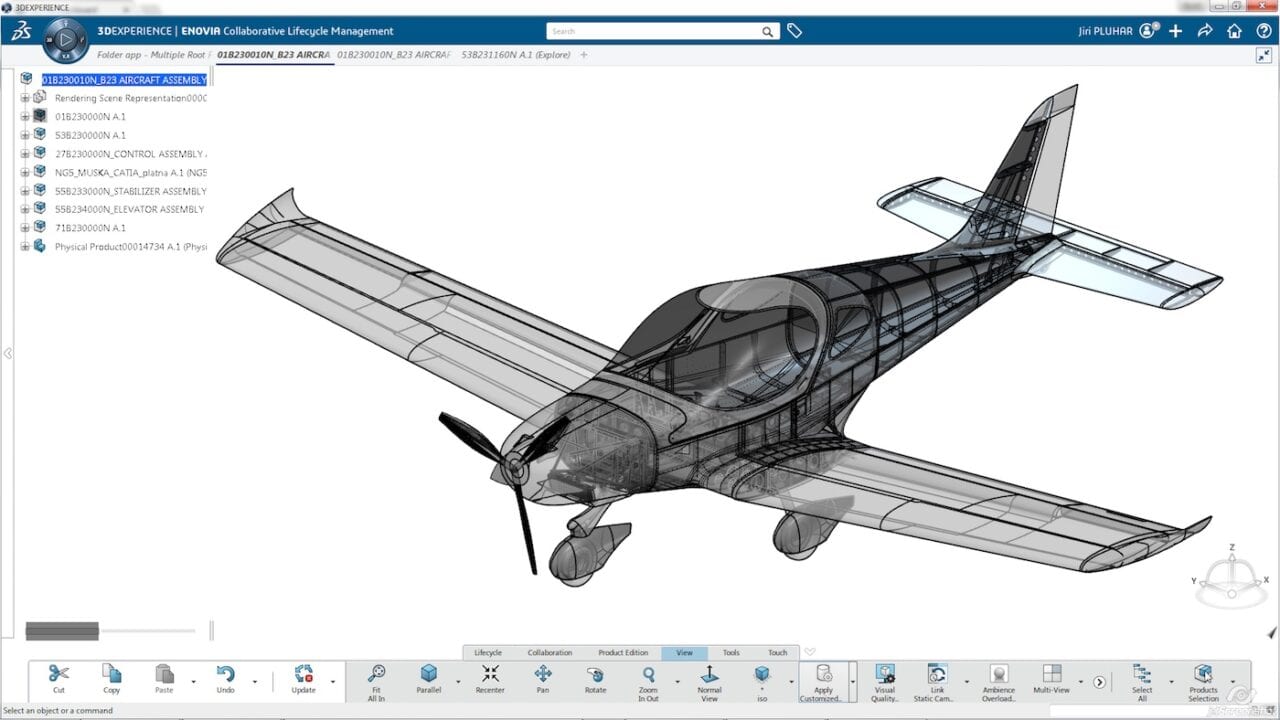
4.2. Automotive & Aerospace
CAD is key for designing vehicle bodies, chassis, drivetrains, interiors, and aerodynamic parts. These industries demand complex modeling and rigorous testing. CAD enables shape simulation, part interaction checks, and seamless integration with CAE tools. CATIA is the industry standard, used globally for its all-in-one platform for design, analysis, and manufacturing.
4.3. Electrical & Electronics
In electronics design, CAD is used for enclosures, component layout, cooling systems, and mounts. When combined with ECAD (electronic CAD), engineers can ensure compatibility between circuit boards and enclosures, avoiding assembly errors. CAD also helps with design optimization for ease of assembly, maintenance, and safety.
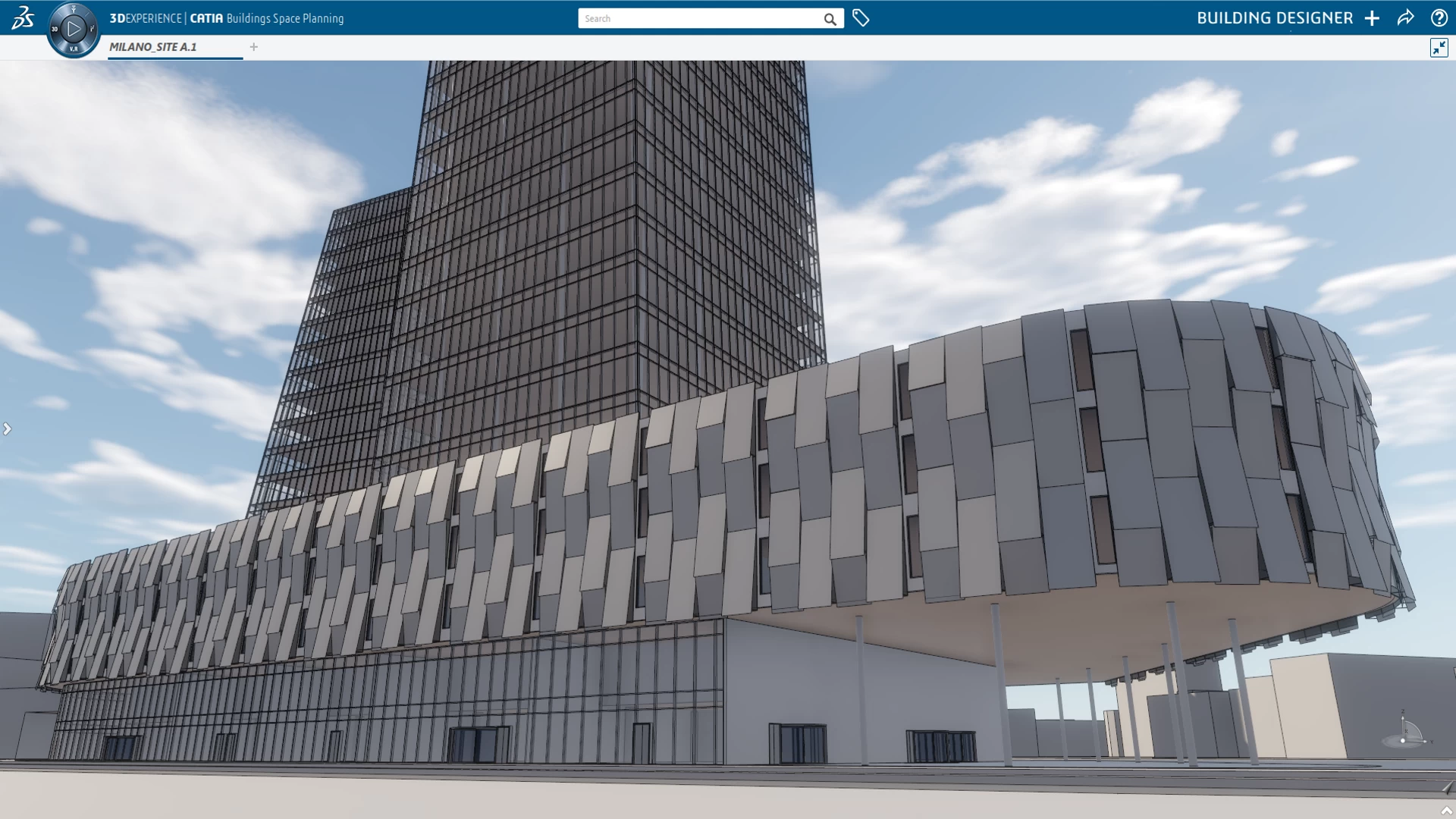
4.4. Construction, Architecture & Structural Engineering
CAD is used for floor plans, elevations, sections, and structural steel models, HVAC systems, piping, and equipment layouts. Engineers use CAD to validate the feasibility of designs before construction. 3D modeling also supports BIM (Building Information Modeling) for synchronized coordination across architecture, structure, and MEP disciplines.
4.5. Medical Devices, Consumer Products & 3D Printing
CAD plays a vital role in designing products with complex geometries like plastic housings, appliances, electronic accessories, and 3D printed parts. In medical device design, simulation of prosthetics, molds, and handheld tools requires extremely accurate, human-compatible designs—made possible with powerful tools like CATIA and CADmeister.
Conclusion
CAD software isn’t just a design tool—it’s a critical foundation for optimizing product development processes in many industries. Whether you're a student, engineer, or business, understanding different types of CAD software, their applications, and how to choose the right one can save time, improve efficiency, and help you stay ahead of technological trends.
If you’re looking for the right CAD solution for your learning or production needs, contact NSV for consultation and hands-on experience with professional design software like CATIA, CADmeister, CADdoctor, and more.
